Common Faults And Treatment Of High-Voltage Electrical Equipment
The focus is on the failures and solutions of 10kV circuit breakers (vacuum, sulfur hexafluoride), disconnectors, busbars, transformers, transformers, cables and arresters. Engineering and technical personnel can refer to this article to analyze and process the accidents of high-voltage electrical equipment to ensure the safe operation of electrical equipment, reduce the impact of accidents, prevent problems as much as possible, and eliminate accidents in the bud.
According to the regulations, the voltage above 250 volts is called high voltage. Here we are mainly talking about 10 kV complete sets of equipment: that is electrical switchgear, metering cabinets, capacitor cabinets, etc. It also includes incoming and outgoing wires and transformers.
TRANSFORMER
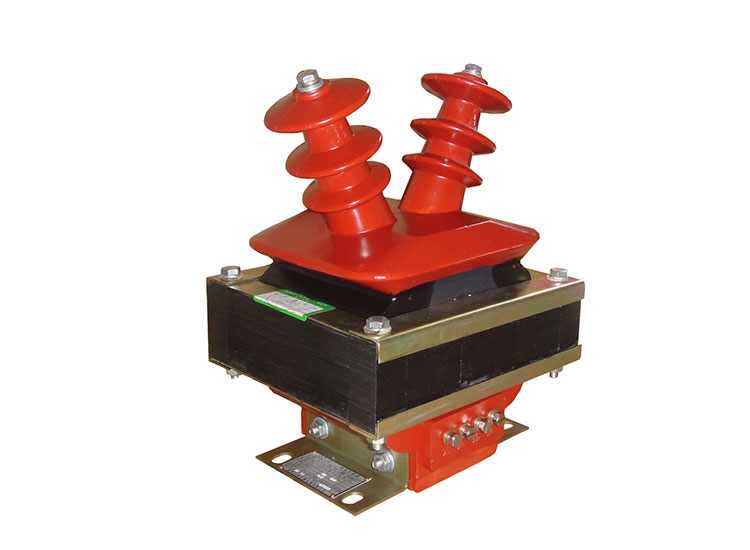

1. Voltage Transformer
Trouble phenomenon: The primary side fuse of the voltage transformer in operation is blown.
(1) Due to faults such as a short circuit between turns, between layers or between phases, and a phase grounding within the voltage transformer sensor, the fuse may be blown.
(2) When the secondary circuit fails (the secondary side of the transformer is faulty), the secondary side fuse is selected too large and the primary side fuse is blown.
(3) The 10kV phase is grounded. When one phase of a 10 kV system is grounded, the ground voltage of the other two phases rises by a factor of three. For a voltage transformer connected to Y0/Y0, its normal two-phase-to-ground voltage will become a line voltage. Due to the increase in current caused by the increase in voltage, the fuse may be blown.
(4) Ferroresonance occurs in the power system. In recent years, due to the massive increase in power distribution lines, cables and users. Great changes have taken place in the electrical parameters of the 10 kV power distribution system. Resonance conditions have gradually formed, and some voltage transformers have poor excitation characteristics. Therefore, ferromagnetic resonance overvoltage often occurs, and overcurrent will be generated on the voltage transformer when the power system is resonant, which not only causes the fuse of the primary side to break, but also often causes the voltage transformer to burn out.
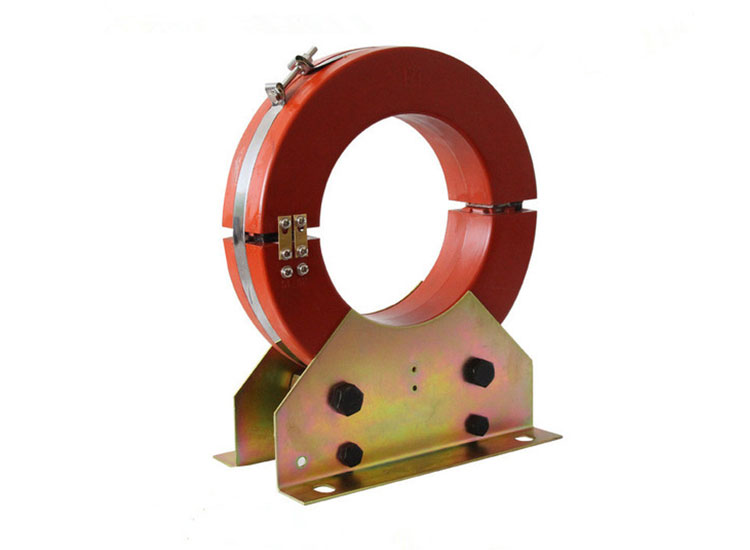
2. Current Transformer
Trouble phenomenon: The current transformer is running due to the overheating of the iron core.
Analysis and processing: The inductive transformer in operation will cause abnormal sound in the case of overload, secondary open circuit, and insulation damage and discharge. Partial corona caused by uneven application of semiconductor paint and loose screws clamping the iron core can also cause loud noises.
The overheating of the iron core of the current transformer may be caused by long-term overload or the open circuit of the secondary circuit causing the iron core to be saturated.
If the above-mentioned abnormal phenomenon is found, firstly, it should be carefully observed, and the cause of abnormal sound or overheating of the iron core should be judged through the instructions of the instrument. If it is caused by overload, reduce the load to below the rated value and observe its operation. If it is caused by the secondary circuit, stop the operation immediately (or reduce the load to the maximum limit). Take necessary safety measures to prevent electric shock during handling. If the discharge is caused by damage to its insulation, it should be replaced.
LIGHTNING ARRESTER
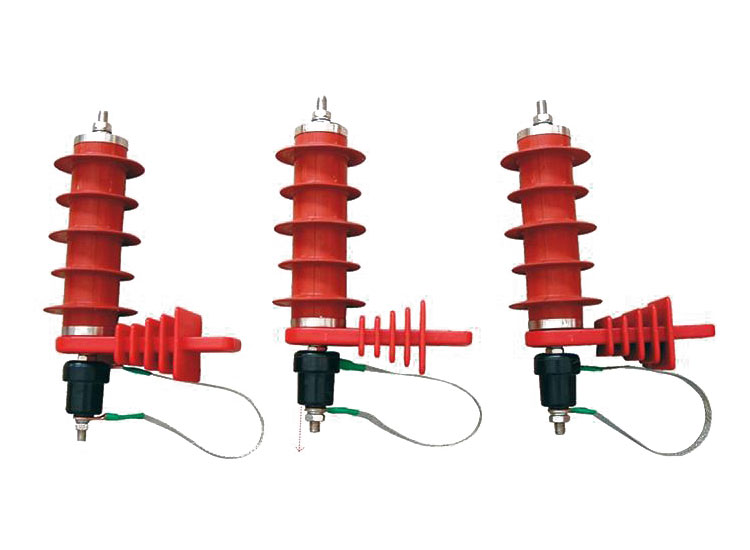
(1) Failure phenomenon: The magnetic insulation is damaged.
Analysis and treatment: The reason for the damage of the magnetic insulation of the arrester in operation should be analyzed and replaced.
(2) Failure phenomenon: explosion occurred during operation.
Analysis and processing: Generally, the characteristics of the arrester are changed due to the poor sealing of the arrester and the damp. Because zinc oxide arresters have good volt-ampere characteristics, they are being widely used. Lightning arresters are relatively low in failure, so annual inspections and pre-tests should be strengthened.
CABLE
Fault phenomenon: single-phase grounding short-circuit, two-phase and three-phase grounding short-circuit.
Analysis and processing: Because the power cable belongs to another profession, and the fault of the power cable is a short circuit between phases. Even if it is a single-phase short circuit, due to long discharge time and other reasons, it will quickly develop into a two-phase or more short circuit. Therefore, it is necessary to find out the reason for the cable line trip and deal with it before sending power, otherwise it may cause more accidents. The treatment method is to check the fault point, then deal with it, do a test after the treatment, and then send the power after passing the test.
