The Importance of Submarine Optical Cables
Today’s society has been covered by various networks, and the network has closely linked all countries in the world, and the subsea optical cable is the main artery to ensure the interconnection between major regional networks around the world. So how important is the undersea cable, and will the US economy collapse once it is cut off?

The undersea optical cable has not been around for a long time. The world’s first submarine optical fiber cable was built in 1988. This optical cable connects Europe and the United States, with a total length of 6,700 kilometers.
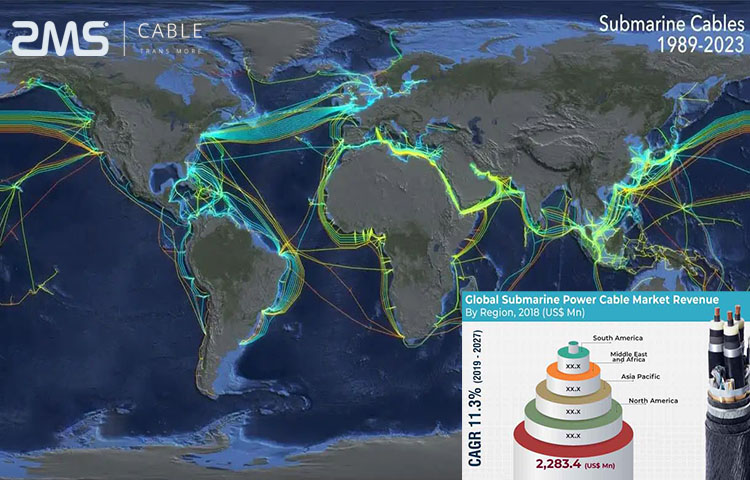
Up to now, more than 90% of the world’s cross-border data transmission relies on submarine communications cables.
According to statistics, the total length of the global deep-sea fiber optic cable has reached 900,000 kilometers, which can circle the earth 22 times.
While the United States enjoys the enormous geographical advantages that the ocean brings to it, it also faces the disadvantage of being far away from major continents. Due to the relatively low cost of shipping, the economic and trade impact is not serious.
But if you want to maintain smooth communication with the world, you can’t do without fiber optic cable in the ocean.
More than 95% of the world’s transoceanic communications require the help of ocean fiber optic cables. Once the deep ocean optical cables are damaged, the communication between the United States and the world will be seriously affected.
The special geographical location of the United States means that the security of the submarine fiber cable network does have a great impact on the information security of the United States.
According To ZMS Statistics, More Than 90% Of The World’s Large Servers Are Located In The United States
ZMS Cable Manufacturing Company has accumulated experience and technology in challenging difficult construction projects all over the world.
We can provide a complete set of optimal solutions from our extensive track record in seabed surveying, design, installation, and protection.
Not only has a great impact on the United States, but also impacts other countries.
Because the world’s only ipv4DNS main root server is located in the United States, once the US submarine internet cable is cut, the global DNS will be impacted.
Although multiple secondary root servers have been set up outside the United States, they can only guarantee access for some users.
If the underwater internet cable is cut off, the major DNS service providers should have prepared plans, and the impact on individual users will not be too great.
But for many multinational companies, such as securities, banks, and other international institutions.
If a large amount of data from these institutions cannot interact with the servers in the United States, it will directly lead to business stagnation and even bring about a lot of losses.
In addition, large technology Internet companies such as Google in the United States are also building internet cables under the ocean, and will soon build a submarine optical cable network.
This also means that as their investments in related facilities such as undersea internet cables continue to increase, these American Internet companies will have stronger control over the Internet in the future.
If these subsea optical fiber cables (Câble Sous-marin) are cut off, these Internet companies will also suffer huge losses in a short period.
To prevent this from happening, the United States is also looking for alternatives to internet cables in the ocean.
For example, in the “Star Chain” plan, various space-based Internet solutions are being tested. However, the satellites in the Starlink plan are WIFI routers, and their function is to connect the terminal to the local backbone network.
Although it can solve network problems in a short time, fundamentally, transoceanic space-based communication technology is not at the same level as submarine communications cable in terms of bandwidth, delay, and anti-interference.
The satellite laser broadband communication being developed at this stage is not mature enough and is easily interfered with, so it cannot meet the needs of intercontinental communication at all. In other words, in the next 3 to 5 years, submarine optical cables will still be an irreplaceable means of transoceanic communication.
Damage and Repair of Submarine Fiber Optic Cable
Submarine fiber optic cables in the deep sea are highly customized products, not only must be able to withstand high-level voltage internally but also have the ability to resist corrosion and wear externally due to being in the deep sea.
It is very easy to destroy a subsea fiber optic cable, but it is not so easy to repair a subsea optical cable. When the deep sea fiber optic cable is damaged, a professional maintenance ship will rush to the scene.
If the underwater fiber optic cable is in shallow water, a robot can be dispatched into the water to drag the fiber optic cable in the deep sea to the surface.
If it is a deep-sea area above 6,500 feet (about 1,980 meters), the repair boat will use a specially-made grapple to grab the ocean fiber optic cable and then lift it to the surface for repairs. Sometimes grappling hooks cut through damaged submarine fiber optic cables, and repair boats raise both ends out of the water for repairs.
Summarize
Having said that, we will know how important the submarine optical cable buried deep in the sea is. Once it is cut off, it will have a huge impact on the US economy.
But whether the United States can collapse is probably related to the number of fiber optic cables that are cut off. There are many fiber optic cables connecting the United States and the world. It may not be realistic for Russia to cut all of these undersea communication cables by itself.
At present, the submarine network carries more than 99% of the data traffic of intercontinental communication and has become an important part of the entire optical communication infrastructure.
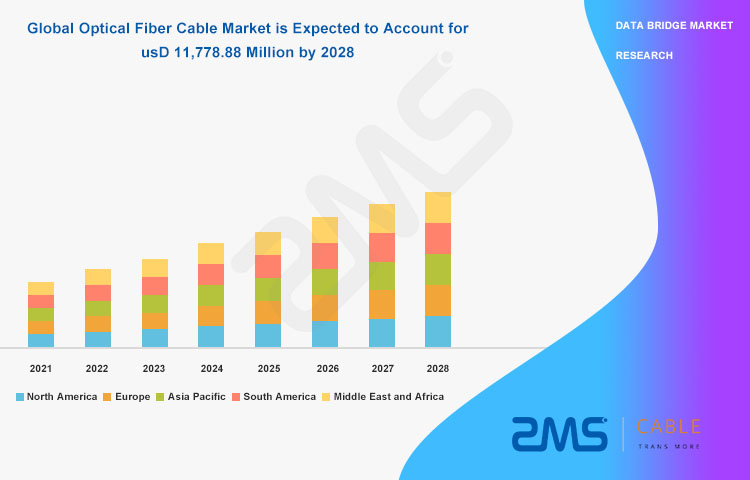
For various marine optical cable application scenarios, ZMS Cable has launched a variety of optical fiber products, including but not limited to armored submarine optical fiber cables, light submarine optical fiber cables, and medium and high voltage power submarine optical fiber cables (HVDC cable and HVAC cable).
Seeking a balance between ultra-low loss and cost optimization, it is suitable for marine space division multiplexing (SDM) systems with and without repeaters.
Providing the largest effective area and ultra-low attenuation coefficient can support the largest single-cell capacity.
Provides industry-leading attenuation performance, suitable for ultra-long-distance high-speed SDM systems.
—ZMS Cable Group
