In the realm of electrical engineering and construction, flexible cables play a pivotal role in ensuring efficient power transmission and connectivity. These cables are designed to withstand various environmental conditions while maintaining their flexibility, making them essential components in numerous industries and applications. From powering machinery in manufacturing plants to enabling connectivity in consumer electronics, the versatility of flexible cables is unmatched. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of flexible cables, exploring their importance, characteristics, applications, and technological advancements.
Importance of Flexible Cables
Flexible cables serve as lifelines in modern industries, facilitating the seamless transmission of power and data in diverse environments. Their importance lies in their ability to withstand constant movement, and bending. And twisting without compromising their functionality. Unlike rigid cables, which are prone to damage when subjected to frequent flexing, flexible cables are engineered to endure repetitive motions, making them ideal for dynamic applications.
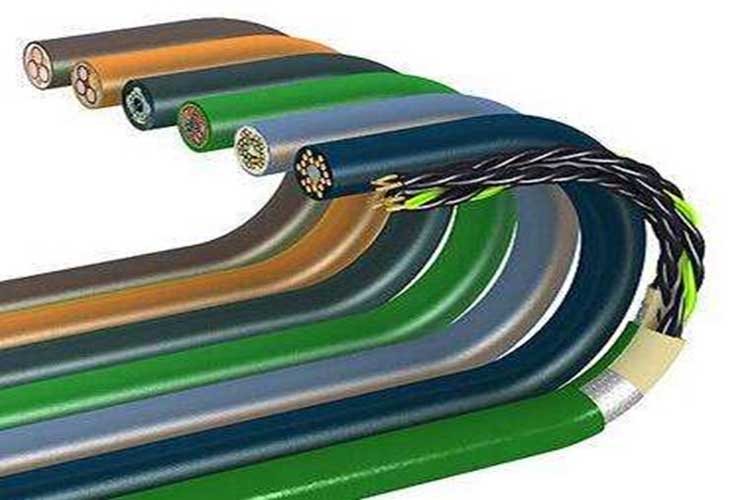
One of the primary advantages of flexible cables is their adaptability to various installation scenarios. Whether it’s navigating tight spaces, accommodating irregular routes, or enduring harsh conditions. These cables offer unparalleled flexibility, ensuring reliable performance in challenging environments. This adaptability simplifies installation processes and enhances overall system reliability, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
Furthermore, these can provide crucial support for portable and mobile devices, enabling mobility without sacrificing connectivity. Devices such as smartphones, laptops, and medical equipment rely on flexible cables to transmit power and data efficiently while withstanding frequent handling and movement. Additionally, flex cables play a vital role in automotive applications, powering electronic components and systems within vehicles while enduring vibrations and temperature fluctuations.
Characteristics of Flexible Cables
Several key characteristics distinguish flexible cables from their rigid counterparts, making them suitable for a wide range of applications:
Flexibility
Perhaps the most defining characteristic of rubber cables is their ability to bend and flex without compromising their structural integrity. This flexibility is achieved through the use of specialized materials and construction techniques, allowing the cables to withstand repetitive movements without breaking or deforming.
Durability
Flexible cables are engineered to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including exposure to moisture, heat, cold, and mechanical stress. These cables ensure long-term reliability in demanding applications by incorporating durable materials such as high-grade insulation and robust sheathing.

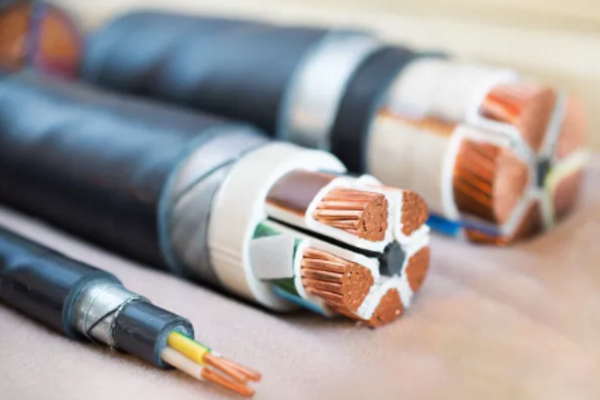
Conductivity
Maintaining optimal electrical conductivity is essential for flexible cables, as any impedance or resistance can lead to power loss or signal degradation. Therefore, these cables are designed with high-quality conductive materials, such as copper or aluminum, to minimize electrical resistance and maximize efficiency.
Size and Weight
Flexible cables are typically lightweight and compact, making them suitable for applications where space is limited or weight restrictions apply. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in industries such as aerospace, robotics, and wearable technology, where minimizing bulk and weight is critical.
Flex Life
The flex life of a cable refers to its ability to withstand a specified number of bending cycles without failure. Flexible cables are rigorously tested to ensure they meet or exceed industry standards for flex life, guaranteeing reliable performance over prolonged periods of use.
Applications of Flexible Cables
The versatility of flex rubber cables enables their deployment across a wide range of industries and applications. Some common applications include:
Industrial Machinery
They are extensively used in industrial machinery and automation systems to transmit power and control signals. From robotic arms to conveyor belts, these cables enable seamless operation while withstanding the rigors of industrial environments.
Renewable Energy
In the renewable energy sector, flexible rubber cables play a crucial role in connecting solar panels, and wind turbines. And other renewable energy sources to power distribution networks. Their flexibility and durability make them well-suited for outdoor installations and harsh weather conditions.
Consumer Electronics
Portable electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops rely on flexible cables to provide power and facilitate data transfer between components. The compact size and flexibility of these cables make them essential for maintaining the sleek and lightweight designs of modern gadgets.

Medical Devices
In the medical field, flexible cables are used in various devices and equipment. Including imaging systems, patient monitors, and surgical instruments. These cables must meet stringent safety and reliability standards to ensure accurate data transmission and patient safety.
Automotive Industry
Flexible cables are integral to the functioning of automotive systems, powering components such as sensors, actuators, and infotainment systems. Their ability to withstand vibrations and temperature fluctuations. And mechanical stress makes them indispensable in automotive applications.
Advancements in Cable flexibility Technology
Advances in materials science, manufacturing techniques, and design methodologies continue to drive innovation in cable technology. Some notable advancements include:
Enhanced Flexibility
Engineers are developing new materials and cable designs to further improve the flexibility of cables, allowing them to bend and flex in even tighter spaces without sacrificing durability or performance.
High-Speed Data Transmission
With the increasing demand for high-speed data transmission in applications such as telecommunications and data centers. These cables are being engineered to support higher data rates while maintaining signal integrity and reliability.
Miniaturization
The trend toward miniaturization in electronics has led to the development of ultra-thin and lightweight flexible cables that can be seamlessly integrated into compact devices without compromising performance.
Environmentally Friendly Materials
There is a growing emphasis on using environmentally friendly materials in cable manufacturing to reduce the environmental impact of production and disposal. Recyclable materials and bio-based polymers are being explored as alternatives to traditional plastics and metals.
Smart Cables
The integration of sensors, microcontrollers, and communication technologies into cables is opening up new possibilities for “smart” cables that can monitor their performance, and detect faults. And communicate diagnostic information to connected systems.
Conclusion

Flexible cables are indispensable components in modern engineering and technology, enabling the transmission of power and data in a wide range of applications. Their flexibility, durability, and adaptability make them essential for industries such as manufacturing, renewable energy, consumer electronics, healthcare, and automotive. ZMS Cable has acquired enough experience after supplying or customizing cables for many customers, plus we have the assistance of a technologically advanced cable factory to help you choose a more suitable cable. As technology continues to evolve, flexible cable designs will likely become even more sophisticated, meeting the ever-changing demands of our interconnected world.