According to a report in the Financial Times (FT.com), market intelligence firm Cru Group recently revealed. A global shortage of fiber optic cables has pushed up product prices and extended lead times for supply. Overshadowing ambitious industry plans for advanced telecommunications infrastructure.
As the report and the ZMS team analysis point out, the timing couldn’t be worse.
Governments around the world have set ambitious targets for rolling out superfast broadband and 5G infrastructure.
Both of these infrastructures will, of course, require massive amounts of fiber optic cable to be laid underground.
Meanwhile, the report notes that companies such as Amazon, Google, Microsoft, and Facebook parent Meta are expanding their data centers around the world.
to meet growing demand, which includes deploying submarine fiber optic cables around the world.
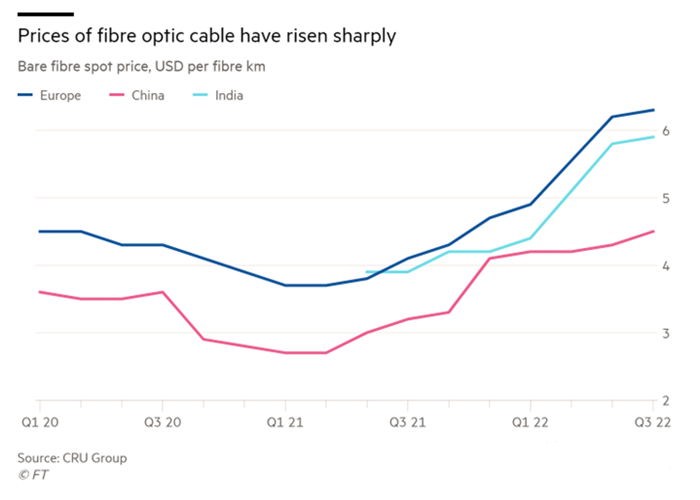
Fiber Prices Reach 3-Year High
Fiber prices have now reached their highest level since July 2019, according to an analysis of data from market intelligence firm Cru.
North America has been less severely impacted than Europe, China, and India, but that may not last long.
In the meantime, the report says, soaring prices have led to significantly longer lead times for fiber, from 20 weeks to nearly a year for small customers.
Ankit Agarwal, managing director of STL, one of the UK’s largest fiber suppliers, told the Financial Times website: “All of us are prioritizing the fastest delivery for our biggest customers.”
Cru Group, for its part, said that Europe, India, and China are among the regions in the world most affected by price increases. The analyst added that fiber costs have risen 70 percent from record lows in March 2021, from $3.70 to $6.30 per kilometer.
This is even though the pandemic has prompted some of the largest technology and telecom groups to cut capital spending.
But a surge in demand for Internet and data services has led to a lack of availability of critical but often overlooked materials.
Many companies Meta and others are expanding their data center empires to meet soaring demand.
This includes laying vast international fiber-optic networks under the sea.
At the same time, governments have set ambitious goals for rolling out superfast broadband and 5G, both of which require massive amounts of fiber optic cable underground.
“Given the sudden doubling of deployment costs, there are now questions about whether countries will be able to meet the targets set for infrastructure development and whether this will have an impact on global connectivity,” said analyst Michael Finch.
Cru estimates that total cable consumption rose 8.1 percent in the first half of the year compared with the same period last year.
China accounted for 46 percent of the total, with North America the fastest-growing region, up 15 percent year-over-year.
Contributing to the shortage is the rising price of some key components of fiber optic technology, in which light is transmitted through flexible fibers with glass cores.
Helium shortages are a key component in fiber optic glass manufacturing.
Partly as a result of plant shutdowns in Russia and the U.S., prices for the element have risen 135 percent over the past two years.
Meanwhile, the price of silicon tetrachloride, another key ingredient in fiber production, has risen 50 percent.
“I’ve never seen an inflationary crisis like this in my career,” said Wendell Weeks, CEO of Corning Incorporated, the world’s largest producer of fiber optic cable.
The company played a major role in inventing the technology in 1970.
Weeks added that the company is increasing production to meet soaring demand from governments, telecommunications companies, and large technology groups, including building new facilities in the United States and Europe.
Fiber prices are now at their highest level since July 2019, according to Cru.
Although North America has not been hit as hard as Europe, China, and India.
A fiber optic cable is a communications cable that consists of two or more glass or plastic fiber cores.
These fiber-optic cores are located within a protective overlay and are covered by a plastic PVC outer sleeve.
Signal transmission along the internal fiber is generally done using infrared light.
In January 2013, Cuba made a change in communications by opening a fiber optic cable to add foreign channels attracting attention.
Here we also need to understand the difference between optical fiber and cable
1. The Difference Between Materials
Cables are made of metal conductors, mostly copper and aluminum, while fiber optics are made of glassy fibers.
2. The Difference In-Transmission Signal
The cable transmits electrical signals. Optical fiber transmits optical signals.
3. The Difference In Application Scope
Cable is now mostly used for energy transmission and low-end data information transmission, such as telephone.
Optical fiber is mostly used for data transmission.
The reason why fiber optic cables have developed so fast that there is a shortage at this time is also because of the very strong safety features that fiber optic cables have developed to date.
1. Testing and Certification
Aluminum cable through the United States of UL, Canada’s CUL, and Australia’s SAIGLOBAI international authority testing certification.
In addition, there are China National Cable and Wire Testing Center, the National Fire Building Materials Quality Supervision and Inspection Center, and other authoritative institutions for testing and certification.
Aluminum alloy conductors meet the requirements of CSA standard C22.2 clause 38 on ACM alloy conductors.
There are also GB12706.1 – 2008 and the latest version of IEC60502.1 performance requirements.
2. Aluminum Alloy Composition Role
The addition of rare piles of earth and iron to the composition of aluminum alloy conductors greatly improves their electrical conductivity and connection properties. Especially when the conductor is annealed the addition of iron produces a high-strength creep resistance.
In case of current overload, iron plays a continuous connecting role so that the aluminum alloy conductor does not creep.
Creep is extremely harmful to cables.
If the cable creeps, its contact point is not tight enough, and the pressure decreases so that the contact resistance increases rapidly, causing overheating at the joint after the current flows through.
If not regularly serviced, there will be a safety hazard.
It is very important to solve the problem of cable creep.
3. Flame Retardant Performance
The insulation material of aluminum alloy cable is flame-retardant silane cross-linked polyethylene.
The process uses a self-locking armor structure, and the heat dissipation performance is far better than the sheath of PVC material, which can quickly dissipate heat. After the flame disappears, the fire can be quickly extinguished and will not delay other materials, so the flame retardant performance is excellent.
Aluminum alloy cable adopts new materials and new technology to ensure its safer use.
The above is some data analysis and introduction to the shortage of optical fiber. For the fiber optic industry leader, after several years of near-tragic price competition, the fiber optic cable industry from a serious volume and price double-kill trough out, opening a new round of boom cycle.

