Electric Cable insulators are critical components in the electrical and telecommunications industries, providing safety, efficiency, and reliability by preventing unwanted electric current from flowing to unintended areas. This comprehensive guide will explore what cable insulators are, their different types and models, and their wide-ranging applications.
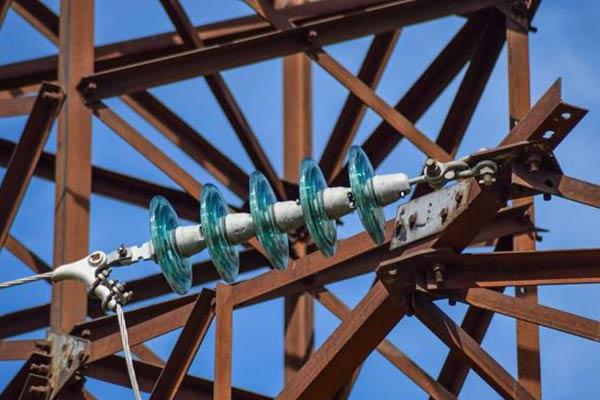

What are Cable Insulators?
Cable insulators are materials used in electrical cables to prevent the unwanted flow of electric current. They serve as protective barriers that isolate the conductors within cables, ensuring that electricity is directed along the intended path. Insulators are typically made from highly resistive materials, such as rubber, plastic, glass, ceramic, or composite materials.
The Importance of Electric Cable Insulators
Cable insulators are essential for:
- Safety: Preventing accidental contact with live wires and reducing the risk of electric shocks.
- Durability: Protecting cables from environmental factors like moisture, heat, and chemicals.
- Efficiency: Minimizing energy loss by preventing the leakage of electric current.
- Reliability: Ensuring that electrical systems operate correctly without interference.
Types of Cable Insulators
Cable insulators come in various types, each designed for specific applications and environments. The most common types include:
1. Ceramic Insulators
Ceramic insulators are widely used in high-voltage applications due to their excellent mechanical strength and high resistance to electrical conductivity. These insulators are typically used in power transmission and distribution systems.
- Applications: High-voltage transmission lines, substations.
- Advantages: High durability, resistance to extreme weather conditions, and good insulation properties.
2. Glass Insulators
Glass insulators are primarily used in outdoor applications where visibility and performance under environmental stress are crucial. They have a high dielectric strength and are resistant to UV radiation, making them suitable for long-term outdoor use.
- Applications: Overhead power lines, telecommunication towers.
- Advantages: Transparency, high resistance to UV light, and low coefficient of thermal expansion.
3. Polymer Insulators
Polymer insulators are made from composite materials, including fiberglass and rubber. They are lightweight, flexible, and resistant to weathering, making them ideal for a wide range of applications, particularly in environments with high pollution levels.
- Applications: Distribution lines, railway electrification, and substations.
- Advantages: Lightweight, flexible, resistant to pollution and vandalism.
4. Plastic Insulators
Plastic insulators, often made from PVC or polyethylene, are commonly used in low and medium-voltage applications. These insulators are cost-effective and offer good insulation properties for general-purpose use.
- Applications: Household wiring, low-voltage industrial applications.
- Advantages: Cost-effective, easy to install, and resistant to moisture and chemicals.
5. Rubber Insulators
Rubber insulators are known for their flexibility and resilience. They are often used in environments where mechanical stress or movement is present, such as in mobile machinery or equipment that vibrates.
- Applications: Automotive wiring, flexible cables in industrial settings.
- Advantages: High flexibility, resistance to wear and tear, and good insulating properties.
6. Composite Insulators
Composite insulators combine the benefits of multiple materials, such as polymer and ceramic. They offer high mechanical strength, excellent insulation, and durability in harsh environments.
- Applications: High-voltage transmission lines, substations, and switchgear.
- Advantages: High strength-to-weight ratio, resistance to pollution and UV radiation, and long service life.
Models of Cable Insulators
Cable insulators come in various models, each designed for specific applications. The selection of an insulator model depends on factors like voltage level, environmental conditions, and mechanical requirements.
1. Pin-Type Insulators
Pin-type insulators are mounted on a pin that is attached to a cross-arm on a pole. They are primarily used in low to medium-voltage distribution systems. These insulators are available in different materials, including ceramic and polymer.
- Models:
- Standard Pin-Type: Used in general-purpose applications.
- Anti-Fog Pin-Type: Designed for areas with high humidity or fog, preventing flashover.
- High-Strength Pin-Type: Reinforced for use in areas with high mechanical stress, such as in coastal regions with strong winds.
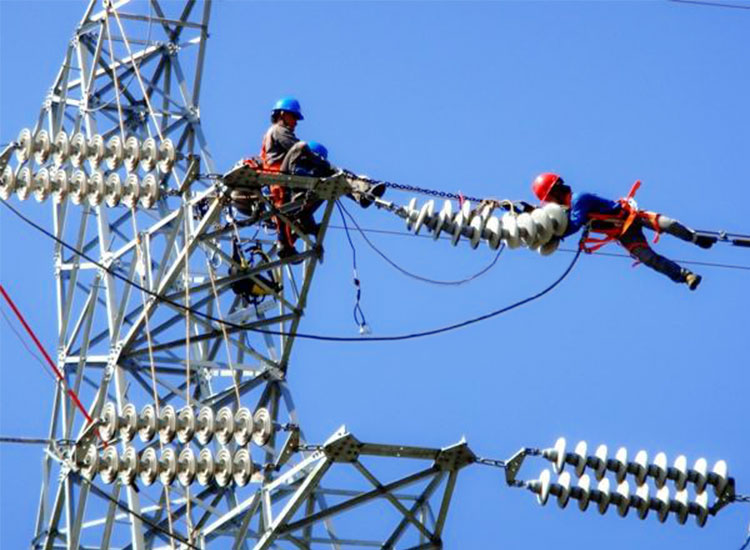

2. Suspension Insulators
Suspension insulators are used in high-voltage transmission lines. They are hung from the cross-arm of a tower and support the conductors. These insulators can be connected in series to form an insulator string, providing the necessary insulation for high-voltage applications.
- Models:
- Standard Suspension Insulators: Used in typical high-voltage transmission lines.
- Double-Shed Suspension Insulators: Offer additional protection in areas with heavy rainfall or pollution.
- Vibration-Controlled Suspension Insulators: Designed to minimize the effects of wind-induced vibrations on transmission lines.
3. Strain Insulators
Strain insulators are used in areas where the conductors experience significant mechanical tension, such as at the end of transmission lines or at sharp bends. They are built to withstand high mechanical loads while providing effective insulation.
- Models:
- Horizontal Strain Insulators: Installed horizontally to counteract mechanical tension.
- Vertical Strain Insulators: Installed vertically for specific applications like anchoring guy wires.
- Heavy-Duty Strain Insulators: Designed for use in extremely high-tension situations, such as long-span transmission lines.
4. Post Insulators
Post insulators are typically used in substations and switchgear. They are mounted on the ground or a structure and support the conductors or busbars. Post insulators are available in various heights and strengths, depending on the voltage and mechanical requirements.
- Models:
- Station Post Insulators: Used in substations for supporting busbars and other equipment.
- Line Post Insulators: Used in medium-voltage overhead lines.
- High-Strength Post Insulators: Reinforced for use in areas with high mechanical stress, such as seismic zones.
5. Shackle Insulators
Shackle insulators, also known as spool insulators, are used in low-voltage distribution networks. They are compact and easy to install, making them ideal for use in confined spaces.
- Models:
- Standard Shackle Insulators: Used in general low-voltage distribution systems.
- High-Temperature Shackle Insulators: Designed for use in environments with elevated temperatures.
- UV-Resistant Shackle Insulators: Designed for outdoor applications where prolonged exposure to sunlight is expected.
Applications of Electric Cable Insulators
Cable insulators are used in a wide range of applications across various industries. Below are some of the key areas where cable insulators play a critical role:
1. Power Transmission and Distribution
Cable insulators are essential in power transmission and distribution systems. They provide the necessary insulation to prevent short circuits and maintain the integrity of high-voltage lines. In these applications, insulators are exposed to extreme weather conditions, mechanical stress, and high voltages.
- Key Uses: Transmission towers, distribution poles, substations, and switchgear.
- Types Used: Ceramic, glass, and polymer insulators.
2. Telecommunications
In the telecommunications industry, cable insulators are used to protect signal cables from electrical interference. Insulators are crucial in maintaining the quality and reliability of communication networks.
- Key Uses: Telephone lines, fiber-optic cables, and communication towers.
- Types Used: Glass and polymer insulators.
3. Railway Electrification
Railway electrification systems use cable insulators to support and insulate the overhead conductors that supply power to trains. These insulators must withstand mechanical vibrations, weathering, and high voltages.
- Key Uses: Overhead catenary systems, substations, and signal systems.
- Types Used: Polymer and composite insulators.
4. Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, cable insulators are used in wiring harnesses to protect electrical cables from short circuits and mechanical damage. These insulators are designed to be flexible and resistant to heat, chemicals, and vibration.
- Key Uses: Wiring harnesses, battery cables, and sensor cables.
- Types Used: Rubber and plastic insulators.
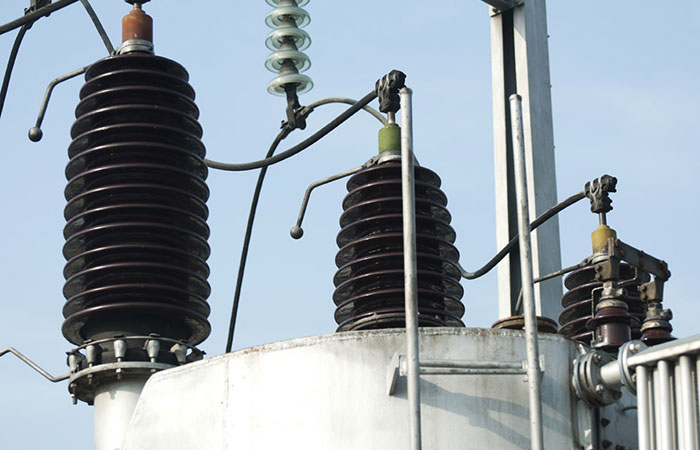

5. Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry requires cable insulators that can perform reliably in extreme conditions, including high altitudes, temperature variations, and radiation exposure. These insulators are used in aircraft wiring systems, spacecraft, and satellites.
- Key Uses: Aircraft wiring, satellite communication systems, and space exploration equipment.
- Types Used: Composite and high-performance polymer insulators.
6. Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, cable insulators are used to protect electrical equipment and machinery from short circuits, electrical interference, and environmental factors. Insulators are selected based on the application’s specific requirements, such as voltage level, mechanical stress, and environmental conditions.
- Key Uses: Factory wiring, machine tools, and heavy-duty equipment.
- Types Used: Rubber, plastic, and composite insulators.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Power Cable Insulators
When selecting cable insulators, it is important to consider several factors to ensure optimal performance and longevity:
1. Voltage Level
The voltage level of the application determines the type and size of the insulator required. High-voltage applications, such as power transmission, require insulators with high dielectric strength and mechanical durability.
2. Environmental Conditions
The environment where the insulator will be used plays a significant role in determining the appropriate material. For example, insulators used in coastal areas must be resistant to salt spray and corrosion, while those used in industrial settings may need to withstand chemical exposure.
3. Mechanical Stress
Insulators in areas subject to mechanical stress, such as wind or vibration, need to be robust enough to handle these forces without compromising their insulating properties. This is especially important in high-voltage transmission lines and railway electrification systems.
4. Pollution Levels
In areas with high pollution levels, such as industrial zones, insulators are more prone to contamination, which can lead to electrical flashovers. Anti-pollution models, such as composite or polymer insulators, are designed to perform better in such environments.
5. Cost and Maintenance
The initial cost of the insulator and the long-term maintenance requirements should also be considered. While some insulators, such as ceramic, have a higher upfront cost, they may offer lower maintenance costs over time due to their durability.
Innovations in Electric Cable Insulator Technology
The field of cable insulators is continuously evolving with advancements in materials and designs.
Recent innovations include:
1. Nanocomposite Insulators
Nanocomposites incorporate nanoparticles into polymer matrices, enhancing the electrical and mechanical properties of the insulator. These materials offer improved resistance to aging, weathering, and electrical stress, making them ideal for high-performance applications.
2. Self-Cleaning Insulators
Self-cleaning insulators are designed to reduce the buildup of contaminants, such as dust or pollution, on their surfaces. These insulators use hydrophobic materials that repel water and dirt, reducing the need for regular cleaning and maintenance.
3. High-Temperature Insulators
High-temperature insulators are designed to perform in extreme temperature conditions, such as those found in aerospace or industrial applications. These insulators are made from advanced materials that can withstand temperatures far beyond the capabilities of conventional insulators.
4. Smart Insulators
Smart insulators are equipped with sensors that monitor the condition of the insulator and the surrounding environment in real time. These sensors can detect issues such as mechanical stress, temperature changes, or electrical faults, allowing for predictive maintenance and reducing the risk of system failures.
Cable insulators are vital components in electrical and telecommunications systems’ safe and efficient operation. Understanding the different types, models, and applications of cable insulators is crucial for selecting the right insulator for a given application. As technology advances, the development of new materials and designs continues to enhance the performance and reliability of these essential components.
Whether you’re involved in power transmission, telecommunications, or industrial applications, choosing the right cable insulator can make a significant difference in the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your systems. By considering factors such as voltage level, environmental conditions, and mechanical stress, you can ensure that your cable insulators provide the protection and performance needed to keep your systems running smoothly.