Understanding technical specifications is crucial to ensuring optimal performance and longevity in cable manufacturing and installation. One such critical specification is the cable bend radius. But what does this term mean, and why does it hold such significance in cable construction? This article explores the concept of cable bend radius, its role in cable design, and its impact on various applications.

What Is Cable Bend Radius?
Cable bend radius refers to the minimum radius a cable can be bent without causing damage to its internal components or degrading its performance. It is typically expressed as a ratio of the cable’s diameter, such as “10 times the cable diameter.” For instance, if a cable is 10 mm in diameter, a bend radius of 10x would mean the cable can be safely bent to a radius of 100 mm.
The Importance of Cable Bend Radius in Construction
Understanding and adhering to the cable bend radius is essential for multiple reasons:
- Preserving Signal Integrity
- In data transmission cables, excessive bending can disrupt the precise alignment of conductors, leading to signal degradation or complete failure.
- Preventing Physical Damage
- Overbending can cause mechanical stress, cracking the cable’s insulation, or even breaking the internal wires, compromising functionality.
- Ensuring Compliance with Standards
- Regulatory bodies and industry standards often specify the required bend radius for different cable types, ensuring safety and reliability.
- Extending Lifespan
- Proper bending maintains the cable’s structural integrity, reducing wear and tear over time.
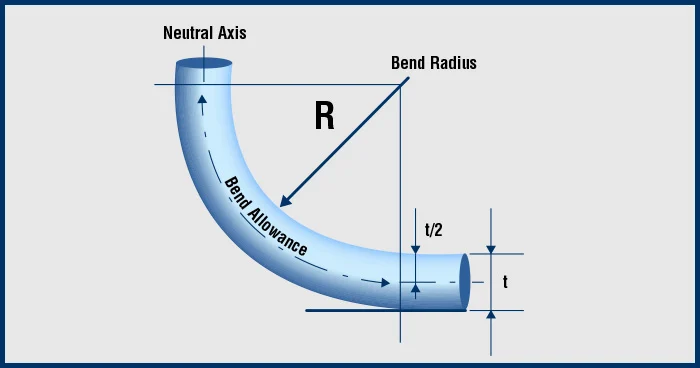
Factors Influencing Cable Bend Radius
Several factors determine the recommended bend radius for a specific cable:
- Cable Type
- Fiber optic cables, coaxial cables, and power cables have varying bend radius requirements due to differences in construction and material properties.
- Outer Jacket Material
- The flexibility of the cable jacket plays a significant role. More pliable materials allow for tighter bends.
- Internal Construction
- The arrangement and type of conductors (solid or stranded) impact how much stress a cable can endure.
- Environmental Conditions
- Temperature and humidity levels can influence the material’s flexibility and overall performance under stress.
Cable Bend Radius Across Different Applications
Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables are particularly sensitive to bending due to their glass core, which can crack or misalign under stress. Manufacturers often specify a minimum bend radius for both installation and long-term static use.
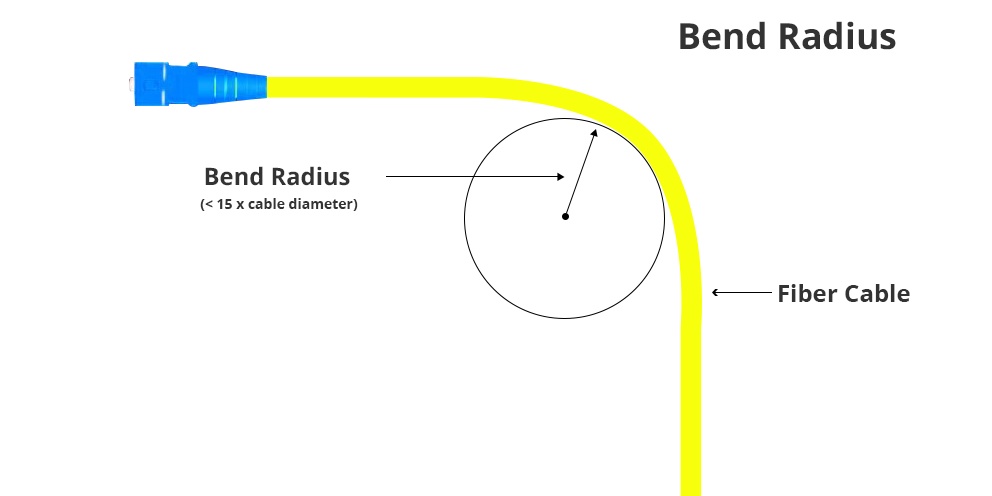
Coaxial Cables
Used extensively in telecommunications and broadcasting, coaxial cables rely on precise alignment of their core and shielding. Adhering to the bend radius ensures consistent signal transmission.
Power Cables
High-voltage power cables have strict bend radius guidelines to avoid insulation breakdown, which could lead to short circuits or fires.
Industrial Cables
In industrial settings, cables are frequently subjected to dynamic movements. Designing cables with an appropriate bend radius helps withstand repetitive flexing without damage.
How to Calculate and Measure Cable Bend Radius
- Manufacturer Specifications
- Always refer to the technical datasheets for the recommended bend radius.
- Practical Measurement
- To measure, form the cable into a circular arc and determine the radius of the curvature.
- Using Multipliers
- For ease, many manufacturers provide a multiplier (e.g., 6x the diameter) to quickly calculate the radius.
Role of Cable Bend Radius in Construction and Design
- Cable Installation
- During installation, adherence to the bend radius ensures cables are not overstressed, particularly in tight spaces.
- Routing and Layout
- Proper planning for cable trays, conduits, and cable runs incorporates bend radius considerations to avoid sharp turns.
- Dynamic Applications
- In robotics and machinery, cables are designed to flex repeatedly. A well-calculated bend radius ensures durability.
- Underground and Submarine Cables
- These cables often experience additional mechanical stress. Adhering to bend radius specifications is crucial to prevent faults.
Consequences of Ignoring Cable Bend Radius
Failing to follow bend radius guidelines can result in:
- Performance Issues
- Reduced data transmission speeds or signal loss.
- Structural Failures
- Fractured insulation or broken conductors.
- Safety Hazards
- Increased risk of electrical fires or short circuits.
- Increased Costs
- Premature cable replacements and system downtime.
Industry Standards for Cable Bend Radius
Several organizations provide guidelines for bend radius across different cable types. Examples include:
- TIA/EIA Standards
- Telecommunications standards specify bend radii for fiber optic and copper cables.
- IEEE Standards
- Power and industrial cables have recommendations for safe bending.
- Manufacturer Guidelines
- Individual manufacturers may have proprietary standards, especially for specialized cables.
Best Practices for Managing Cable Bend Radius
- Plan Ahead
- Incorporate bend radius requirements during the design phase of projects.
- Use Cable Management Systems
- Cable trays, conduits, and strain reliefs can help maintain appropriate bending.
- Train Installers
- Educating technicians on the importance of bend radius prevents mishandling.
- Inspect Regularly
- Periodic inspections can identify bends that exceed the recommended radius.
The cable bend radius is a critical factor in cable design and installation, ensuring performance, safety, and longevity. By understanding its importance and adhering to guidelines, industries can avoid costly errors and maintain system integrity. Whether you’re working with fiber optics, coaxial cables, or high-voltage power lines, respecting the bend radius is non-negotiable for reliable operations.
By emphasizing the significance of the cable bend radius, professionals can implement best practices and optimize the functionality of their installations.