In recent years, as global information technology has advanced rapidly and energy demand has increased, our lives have undergone significant changes. Since the large-scale adoption of electricity in the 19th century, power has reached virtually every corner of the world, greatly facilitating daily life. However, the rising cost of electricity has also become a significant burden for many households.
Statistics show that, on average, global household electricity prices have increased by nearly 30% in the past decade. For example, in Germany, the average electricity price rose from around €0.28/kWh in 2013 to €0.40/kWh in 2023. In the UK, electricity costs climbed from approximately £0.184/kWh in 2010 to around £0.358/kWh in 2024.
Against this backdrop, solar system installation has gradually entered thousands of homes, seen as an ideal solution to reduce electricity bills and promote sustainability. But is residential solar system installation difficult? And is it truly cost-effective compared to skyrocketing electricity prices? Let’s dive in with ZMS Cable.

Best Conditions for Solar System Installation at Home
Roof Type and Area
a. Roof Type
- Best: South-facing, west-south-facing, or east-south-facing pitched roofs are ideal for installing solar panel systems. Flat roofs are also feasible.
- Not recommended: Complex roof structures with multiple skylights or obstructions can increase installation costs and risks.
b. Roof Area
- Typically, about 6-8 square meters of usable roof space is needed for every 1 kW of solar system capacity. For a 3kW solar panel system, approximately 18-24 square meters is required.
Orientation
Best Orientation: South-facing (in the Northern Hemisphere)
A south-facing roof captures maximum annual solar energy output. East-south or west-south orientations are also possible, though they may have around 5-10% lower output, but are still viable.
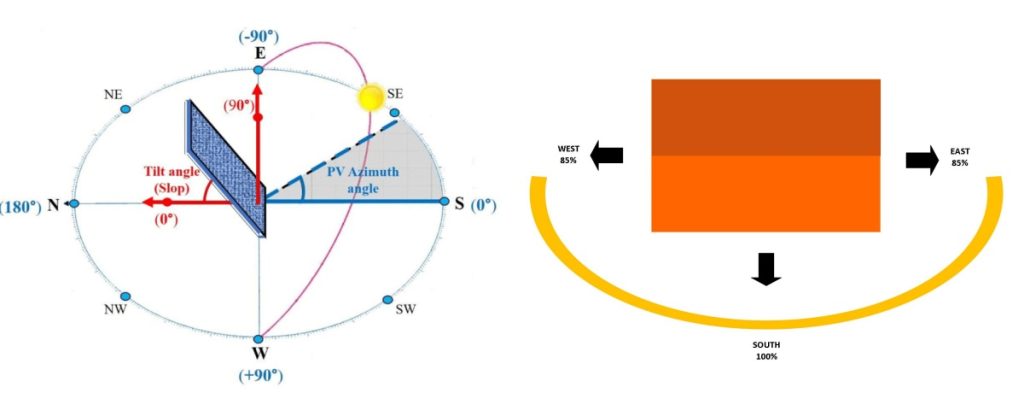
Roof Tilt Angle
Optimal Tilt Angle
Generally, the optimal tilt is close to the local latitude (e.g., 39°N in Beijing suggests a 30°-40° tilt). A steeper angle captures more winter sun; a shallower angle captures more summer energy—interesting, right?
Shading
No Obstructions
Ensure no tall buildings, trees, poles, or other structures block sunlight, especially between 9 AM and 3 PM, the prime generation hours. Even partial shading can reduce overall efficiency.
Roof Load-Bearing Capacity
Structural Requirements
The roof must support the weight of the solar panels and mounting system. Most residential roofs can handle an extra load of around 15-20 kg/m², but older buildings or special materials (like corrugated steel) should be assessed by professionals.
Grid Connection
Grid-Tied Systems
Selling excess electricity back to the grid requires approval from your local utility company. Off-grid systems, on the other hand, need battery storage, which adds significant cost.
Policies and Permits
Incentives and Subsidies
Many countries and regions offer financial incentives, tax credits, or rebates for residential solar system installation, making the investment more affordable. Check local regulations, application processes, and required permits in advance.
Other Environmental Factors
Climate
Solar systems are generally adaptable, but regions with frequent rainfall or overcast weather may see reduced performance. However, modern solar panels can still generate electricity from diffuse light, so they work even in cloudy conditions.
How Much Does a Residential Solar System Installation Cost?
The total cost of a solar panel system installation depends on system size, brand, component quality, local labor costs, and available subsidies.
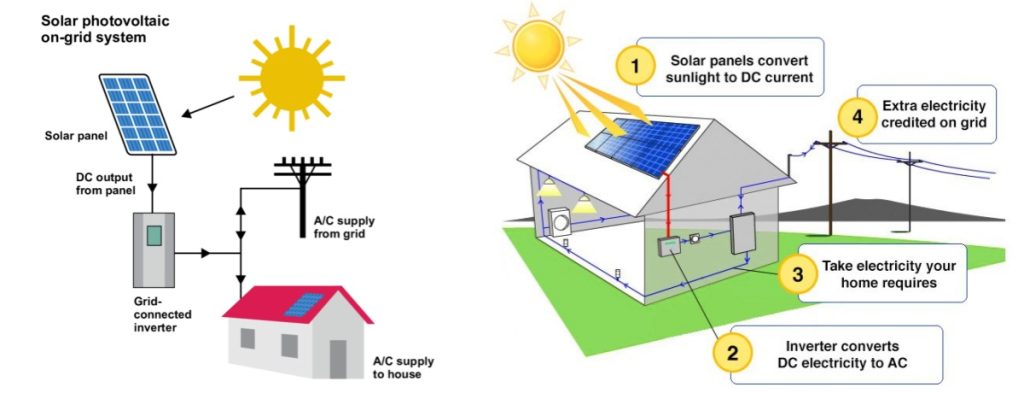
Let’s break down the costs with examples from ZMS Cable’s 2024 solar projects:
Typical System Sizes and Prices
- 3kW System: Suitable for basic household needs
- Cost: approximately $3,500 – $4,900
- 5 kW System: For families with higher electricity consumption (air conditioning, water heaters, heating)
- Cost: approximately $5,500 – $7,700
- 10kW System: Ideal for villas or small commercial use
- Cost: approximately $9,700 – $14,000
In developed countries, prices may be higher, for example, in the US, around $3-4 per watt. Germany and the UK often have higher costs, influenced by taxes and subsidies.
Cost Breakdown
- Equipment (60%-70% of total cost):
- Solar panels
- Inverter
- Solar cables and electrical accessories (such as DC/AC distribution boxes)
- Mounting structures and connectors
- Choosing high-quality solar cable is crucial for safe, efficient, and long-lasting system performance.
- Labor and Installation (20%-30% of total cost):
- Site survey, design, installation, wiring, and inverter connections
- Solar cable installation and system wiring
- Other Costs (5%-10%):
- Grid connection fees (if applicable)
- Insurance (such as fire protection)
- Annual maintenance fees (usually low), which can often be covered by product warranties.
Why High-Quality Solar Cable Matters
Solar cable acts as the backbone of your solar system installation, linking all components to harness the sun’s power. These cables connect the solar panels, the inverter, and the distribution box. Because solar systems are exposed to outdoor conditions, they require cables that are UV-resistant, heat-resistant, and flame-retardant.
- Common types include H1Z2Z2-K and EN 50618.
- High-quality solar cables reduce power loss, lower fire risks, and extend system lifespan.
- Poor-quality cables may lack essential certifications, leading to potential failures and losses.
Steps for Residential Solar System Installation

Site Survey
- The installation team inspects the roof structure, orientation, shading, and load-bearing capacity.
System Design
- The design team tailors the solar system to your energy needs, budget, and roof area, including panel layout, inverter selection, and solar cable installation.
Equipment Procurement
- Purchase solar panels, inverters, mounting systems, solar cables, and other essential accessories from reliable suppliers.
Wiring and Installation
- The crew installs the support structures, mounts the panels, runs the solar cables, and completes all electrical connections, ensuring safety, durability, and aesthetics.
Grid Connection
- After system testing, apply for grid connection approval (if needed) and ensure the system operates smoothly.
Advantages of Residential Solar System Installation
Lower Electricity Bills:
Generate your power during the day and offset expensive grid electricity. Sell surplus power back to the grid in some regions for extra savings.
Environmental Benefits:
Solar energy is clean and renewable, producing no CO2 emissions and reducing your carbon footprint.
Incentives and Additional Income:
Many governments provide incentives for solar system installation, plus the option to sell excess power for profit.
Energy Independence:
Enjoy a self-sufficient power supply, less dependent on traditional grids, especially during outages or unstable supply. Battery storage can add backup power capability.
Long Lifespan and Low Maintenance:
Solar panels typically last 25+ years, requiring minimal maintenance (just occasional cleaning).
With rising electricity costs worldwide, solar system installation has become an increasingly attractive option for households and businesses alike. This guide has explained the essential conditions, cost breakdown, and installation steps to help you plan your solar energy project.
When selecting solar system components, remember that in addition to solar panels and inverters, high-quality solar cable is key. It ensures the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your entire system.
With continuous technological advancements, solar system installation is becoming more affordable and reliable, helping solar power reach more homes around the world.