Submarine fiber optic cable has come to the forefront of many people’s minds as the global power industry has grown by leaps and bounds. People can readily use the Internet and make telecommunication calls all over the world today, all relying on the rapid development of submarine cables. So what exactly is an undersea fiber optic cable? What are the differences and similarities between it and submarine cable in terms of application? The following ZMS cable editorial will take you to understand how to collect it!
About Submarine Fiber Optic Cable
Modern submarine cables use fiber-optic technology. Subsea or submarine cables are fiber optic cables that connect countries across the world via cables laid on the ocean floor. People who do not know much about cables can even think that submarine cables include submarine fiber optic cables.
This is because submarine cables are used for telecommunication transmission. Submarine fiber optic cable is also known as submarine communication cable.
Submarine cables are divided into submarine telecommunication cables and submarine power cables, and modern submarine cables use fiber optics as the material to transmit telephone and internet signals.
In this day and age, people all over the world are accessing the internet every day. By going online, people can keep in touch with the rest of the world and exchange information at any time.
And this net that is on is the internet. The reason why the Internet is inter+net, the network is connected to the network, rather than Intranet, the network within the network, is because of the interconnection between the networks.
Optical technologies of submarine cables consist of sending information in the form of light pulses along a fiber.
Submarine fiber optic cable is to ensure that the global major regional networks can be interconnected between the main artery.
The Birth and Development of Submarine Cables
The birth of underwater fiber optic internet cable is not very long.
People put forward the concept of the submarine fiber optic cable industry has been a long time, but the world’s first submarine cable, until 1988 to built.
This cable connects Europe and the United States, with a total length of 6,700 kilometers, containing three pairs of optical fibers, each pair with a transmission rate of 280Mb / s. The cable was built in 1988, the first submarine cable in the world.
But the big brother of submarine fiber optic cable, submarine cable, was born a long time ago. As early as 1850, the world’s first submarine cable was laid between Britain and France. Today, 173 years have passed, even before the invention of the telephone.
In these 100 years or so, mankind has gone through three industrial revolutions and entered the age of information technology, and it has become completely impossible to leave network communication and data communication behind.
At present, more than 90% of the world’s transnational data transmission is undertaken by undersea fiber optic cables.
According to the statistics of 2023, the number of submarine fiber optic cables in production worldwide has reached 469, with a total length of more than 1.39 million kilometers.
It is expected that from 2023 to 2028, the world will build 153 new submarine fiber optic cable systems, and the length of new submarine cables is about 770,000 kilometers.
Common Types of Submarine Fiber Optic Cables
In the development of the undersea fiber optic cable pandemic, what are the most common types of submarine fiber optic cables?
Submarine Lightweight Fiber Optic Cable(LW)
This lightweight fiber optic submarine cable is part of the URC-1 family. This fiber optic cable is generally applicable to the water depth of 1000-8000m, laid in the sandy seabed with a good and stable environment. Its main feature is that it is structurally unarmored for protection, so it is used when laying on the surface of the seabed, and the seabed conditions are relatively safe.
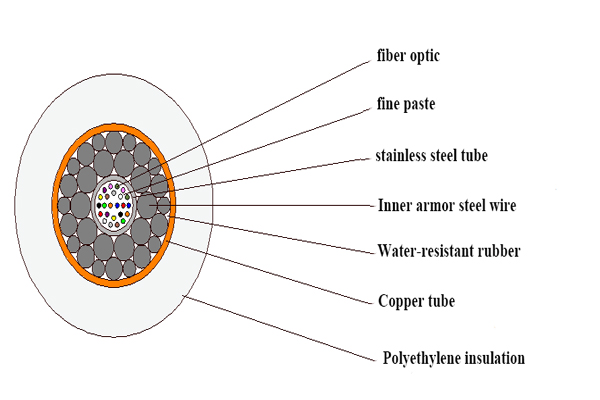
Submarine Lightweight Protection Fiber Optic Cable(LWP)
Light protection fiber optic cable is suitable for laying in the water depth of 1000-8000m, and it is used on the rough surface of the seabed. Because there is one more layer of metal belt armor protection layer device in the structure than ordinary light fiber optic cables, it is more suitable for moderate wear and tear or may be torn by marine animals environment.
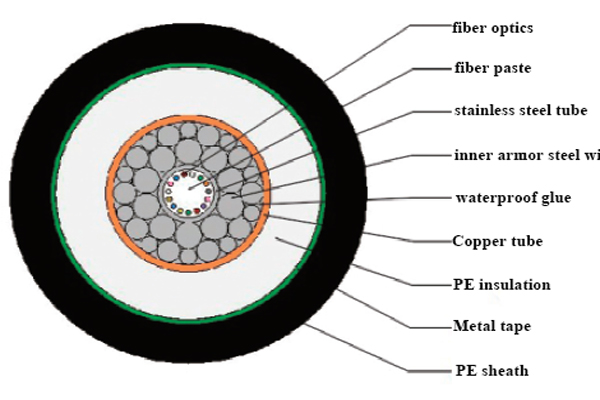
Submarine Single-Layer Armored Fiber Optic Cable(SA)
The single-layer armored mechanism is suitable for water depths of 20-1000m and can be laid in complex rocky terrain, and high-risk tugboat hazardous areas. It is based on lightweight fiber optic cable to increase the diameter of a single layer of steel wire as armor to strengthen the protection of the cable.
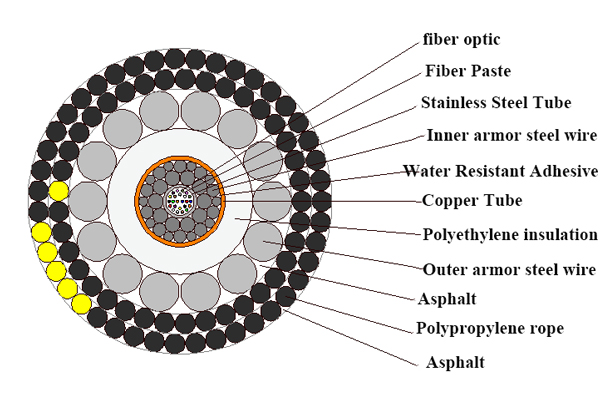
Submarine Double-Layer Armored Fiber Optic Cable(DA)
The single-layer armored structure of the submarine cable is suitable for water depths below 500m and can be laid in complex rocky terrain or areas with high danger of tugboat hazards and high abrasion. The main feature of this kind of cable is that based on a single-layer armored structure, double layers of steel wires of different diameters are added as armoring to strengthen the protection of the cable.
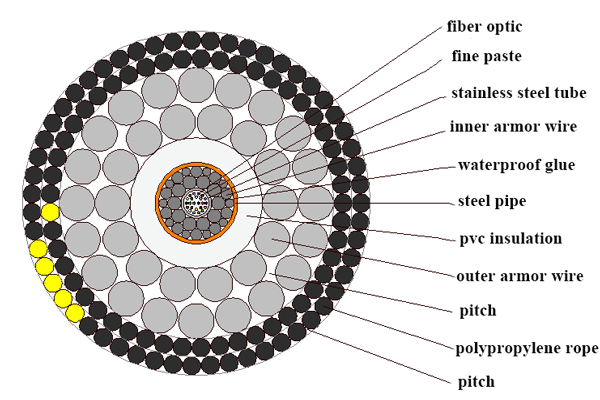
In fact, there are more such as heavy armored submarine cables and direct buried fiber optic cables, etc., if interested, we will introduce them in subsequent articles.
2023 Global Submarine Cable Distribution
Internet information traffic flow and data center distribution dominated the global submarine cable layout changes, and the connectivity of submarine cables within the region continues to enhance, Europe – the United States and Canada, Asia – the United States and Canada, Latin America – the United States and Canada, Asia – Europe, and other traditional large bandwidth demand for the direction of the submarine cable length and the number of submarine cables set to continue to strengthen the emergence of new submarine cable routes so that the submarine cable network architecture is gradually perfected. The capacity of submarine cables in major directions around the world continues to increase, with strong demand for submarine cable upgrades and construction.
The directions with the highest international bandwidth usage are, in descending order, intra-Europe, Europe-U.S. and Canada, intra-Asia, Asia-U.S. and Canada, and Latin America-U.S. and Canada. The directions with the highest CAGRs are, in descending order, Asia-Oceania (57%), intra-Africa (56%), intra-Asia (53%), Africa-Middle East (51%), Asia-Europe (50%), Africa-Europe (50%), and Africa-Europe (50%). ).
A total of 106 submarine cables were delivered globally in 2018-2022, with the number of submarine cables delivered within each region far exceeding the number of submarine cables delivered between regions. First, the level of interconnection between Asian countries has significantly increased, with 29 new submarine cables and 17 submarine cables under construction/proposed to be constructed within Asia, mainly including submarine cables between China, Japan India and Southeast Asian countries, submarine cables between Southeast Asian countries, and domestic submarine cables in Indonesia and the Philippines, such as the ADC and SJC2 submarine cables connecting China, Japan and New Zealand, IAX and MIST submarine cables connecting India and Singapore, and CDSCN submarine cables in the Philippines. CDSCN submarine cable in the Philippines.
