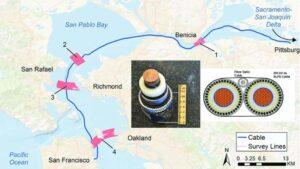
High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) power transmission systems (also known as power highways or electric highways) use direct current (DC) to transmit power versus the more common alternating current (AC) systems. Most HVDC power transmission lines use voltages between 100 kV and 800 kV.
INFORMATION
Welcome to the ZMS CABLE information blog, here is the cable industry knowledge sharing and technology popularization of the professional world. In this section, we focus on cable technology, product applications, and industry knowledge, carefully crafting a series of easy-to-understand and practical content, to provide readers with authoritative technical support and comprehensive industry interpretation.
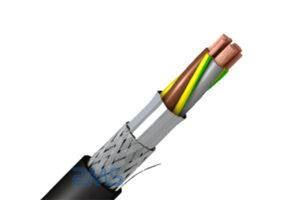
What Do You Mean By Shielded Cable? And What Is A Cable Shield Layer?
The shield on the shielded cable is the cable formed in the way of the transmission cable plus a shield against external electromagnetic interference. The so-called ‘cable shielding’ on the cable structure is also a measure to improve the distribution of electric fields. The cable conductor is made of multiple strands of wire stranded, it is easy to form an air gap between the insulation layer, and the conductor surface is not smooth, which will cause the electric field concentration. Then the following will give you detailed knowledge about shielded cables.
How do Identify The Authenticity of Mineral Insulated Fireproof Cable?
As the mineral insulated fireproof cable for the power transmission of the building engineering fire system, its safety and reliability requirements are very high. It is the “lifeline” of rescue in case of fire, but now the cable industry market is mixed, with fierce competition between peers and overcapacity, which gives unscrupulous businessmen the understanding of the crooked brain. How do distinguish the authenticity of fire-resistant cable?
Control Shielded Cable – Metal Shield And Shield Grounding
Metal shielded control cables are an important measure to attenuate and prevent electrical interference. Including the total shielding of the core, sub-shield, and double-layer type total shielding. The choice of metal shielding type of control cable should be based on the strength of the possible impact of electrical interference, taking into account the comprehensive measures to suppress interference to meet the requirements of reducing interference and overvoltage. The higher the requirements for the anti-interference effect, the greater the corresponding investment. Should be used steel belt armor, steel wire braid total shielding, the price of the cable increased by about 10% ~ 20%.
Selection Of Cable Lines And Cable Cross-Section
Ⅰ. Cable lines in the mine underground due to space constraints and safety needs, in addition to the rack line motor car, are used cable lines
Power cables can be divided into rubber-insulated cables, plastic-insulated cables, and oil-impregnated paper-insulated cables according to the insulation material. At present, oil-impregnated paper-insulated cables are rarely used, so do not speak.
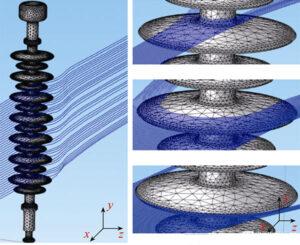
The Droplet Movement And Ice-Covering Characteristics Of The Compound Insulator DC Electric Field
Compound insulator icing has always been a severe problem in the safe operation of my country’s power grid transmission line. It can not only cause the mechanical overload and collapse of the transmission lines and the tower but also cause the ice and flashing collar of the insulator string of the transmission line. In response to the impact of covering the power of power grid transmission lines, domestic and foreign scholars have done a lot of research.
What are The Considerations of Wire and Cable Storage and Transportation?
Storage and transportation of wire and cable products are two very important aspects. If the storage and transportation methods are not appropriate, the quality of wire and cable products can cause damage and affect the safety of use. So, in the storage and transportation of cable products, what matters need our attention?
Carbon Fiber Cable Construction Typical Defects And Operational Considerations
The full name of the carbon fiber wire is carbon fiber composite core aluminum stranded wire (ACCC), the wire from the beginning of this century has only been used for a relatively short period of more than ten years, there is a certain amount of experience in the application. Carbon fiber wire has high strength, lightweight, high modulus of elasticity, small coefficient of linear expansion, small arc sag, small line loss, large capacity (allowing high temperature), corrosion resistance, long service life, and other characteristics. Especially suitable for coastal, mining areas corrosion intensity, high fouling strength, the wire is easy to dance the use of the environment.
7 Common Faults In 10KV Overhead Cable Transmission Lines, As Well As The Causes Of Faults And Preventive Measures
10KV overhead cable transmission line common faults are 7 kinds
1 Single-phase grounding fault
Single-phase grounding is the most common fault in the power distribution system, mostly occurring in wet and rainy weather. Single-phase grounding not only affects the normal power supply of users, but also Hunan Sunshine Electronics School maintenance experts believe that: it may produce overvoltage, burn equipment, and even cause an inter-phase short circuit and expand the accident.
Design, Production, and Installation of Cable Termination and Joints for 10kv Cable Projects
1 Scope of application
It is suitable for the installation of 10kV XLPE cable cold shrink termination and joints in distribution network projects.